Archae Which Survive Best in Environments as Hot as
They are also part of the human. How Hyperthermophiles survive in high temperature.
Archaea The Third Domain Of Life The Santa Barbara Independent
Hyperthermophiles are adapted to hot environments by their physiological and nutritional requirements.

. There is not one basic set of adaptations that works across all environments instead Archaea have evolved protein features that are specifically adapted for each extreme environment. In sulfuric hydrothermal areas it oxidizes sulfur into sulfuric acid which helps dissolve the rocks into mud. In the presence of oxygen Sulfolobus spp.
Archaea of the genus Sulfolobus Figure 1 are thermophiles that prefer temperatures around 7080C and acidophiles that prefer a pH of 23. Other bacteria and archaea are adapted to grow under extreme conditions and are called extremophiles meaning lovers of extremes Extremophiles have been found in all kinds of environments. The archaebacteria kingdom is one of the six kingdoms.
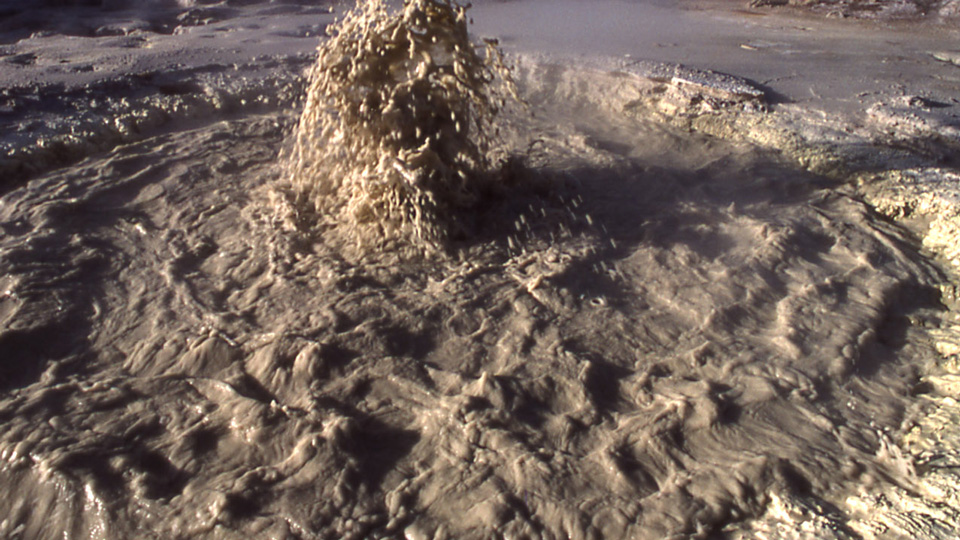
Archaeans include inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on the planet. Whenever you see a hot muddy acidic spring you are probably seeing the results of a thriving community of archaeal cells called Sulfolobus. B hot springs geysers and near volcanoes.
2 Sulfolobus can live in aerobic or anaerobic environments. Use metabolic processes similar to those of heterotrophs. This is the archaea most often isolated and most well known by scientists.
In anaerobic environments they oxidize sulfur to produce sulfuric acid. Archae that can live under extreme conditions Archae that live in extremely hot environments above 80 degre Archae that live in extremely acidic environments. Halophilic archaea may survive for millions of years within brine inclusions in salt crystals.
Organisms in this kingdom are also called Bacteria. Water-containing terrestrial subterranean and submarine high temperature areas harbor a variety of hyperthermophilic bacteria and archaea which are able to grow optimally above 80 degrees C. Archaea that love extremely hot environments live in a hot springs geysers and the desert.
Archaea bacteria are extremophiles living in harsh environments such as hot springs and salt lakes since they have been found in a broad range of habitats including soils oceans marshlands and the human colon so they are ubiquitous. Examples of archaea habitats are boiling hot springs and geysers such as those found in Yellow Stone Park USA and ice such as the Arctic and Antarctic oceans which. Archaea bacteria are extremophiles living in harsh environments such as hot springs and salt lakes since they have been found in a broad range of habitats including soils oceans marshlands and the human colon so they are ubiquitous.
Rennett Stowe flickr. They are unicellular and live in very extreme environments. C hot springs the desert and near the equator.
Click to see full answer. As a consequence cell components like proteins nucleic acids and membranes have to be stable and even function best at temperatures around 100C. D the desert near volcanoes and near the equator.
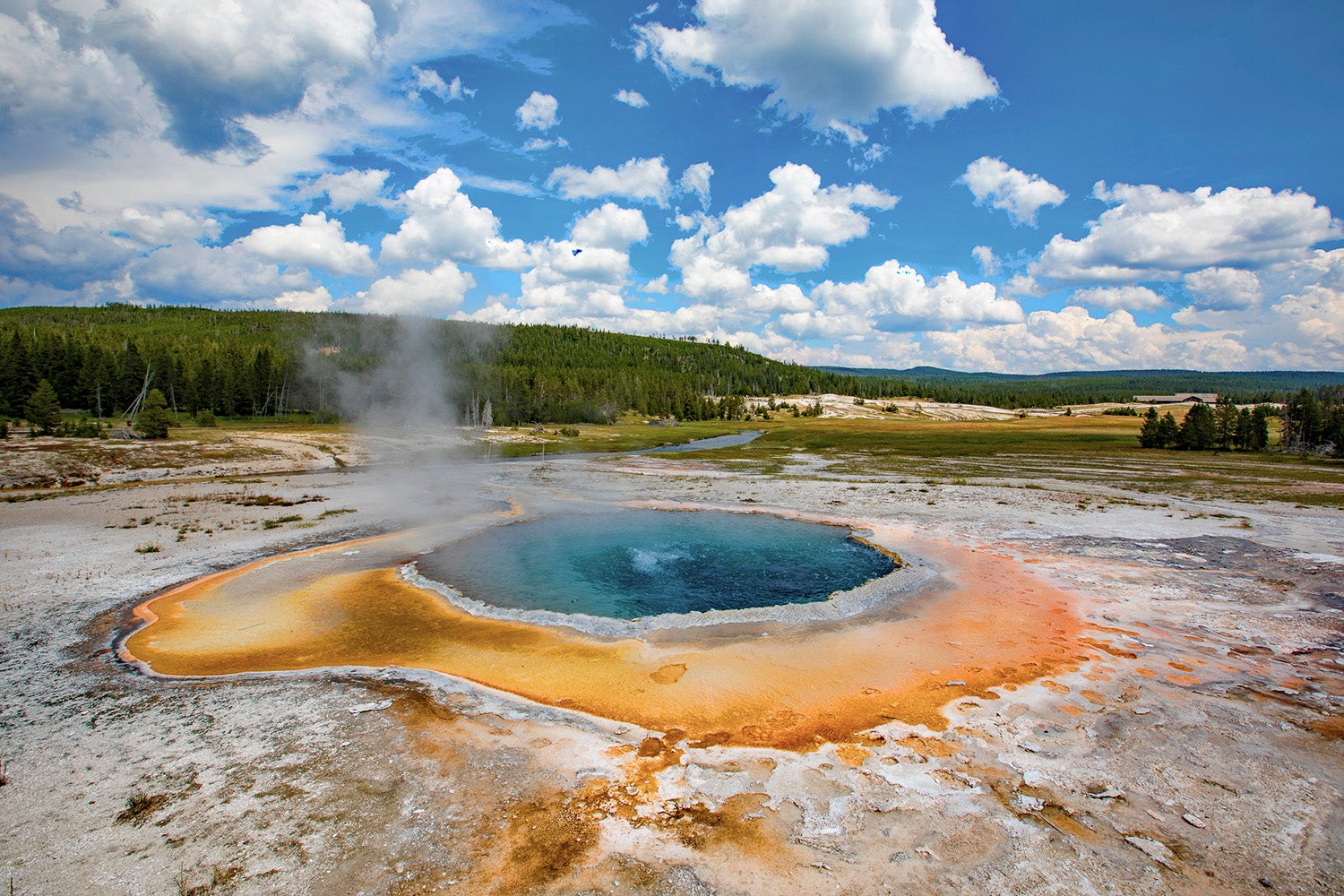
They were also found in a diverse range of highly saline acidic and anaerobic environments. Their cell wall differs in structure from that of bacteria and is thought to be more stable in extreme conditions helping to explain why some archaea can live in many of the most hostile environments on Earth. Others live in hot springs such as the ones pictured above or in extremely alkaline or acid waters.
Click to see full answer. Another magnesium-sulfate-rich environment is Hot Lake WA USA which recently became an. Hyperthermophiles are adapted to hot environments by their physiological and nutritional requirements.
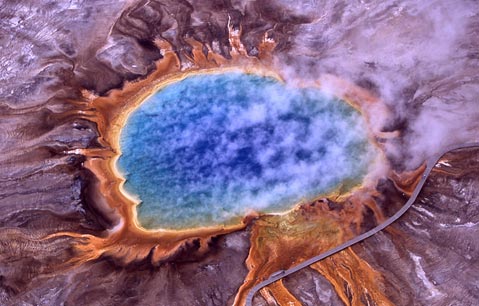
Archaea were initially viewed as extremophiles living in harsh environments such as hot springs and salt lakes but they have since been found in a broad range of habitats including soils oceans and marshlands. Some live near rift vents in the deep sea at temperatures well over 100 degrees Centigrade. The microorganism Sulfolobus acidocaldarius lives in extreme environments such as Emerald Hot Spring in Yellowstone National Park.
The depth of the oceans hot springs the Artic and the Antarctic in very dry places deep inside Earth in harsh chemical environments and in high. Many species have different modes of anaerobic metabolism and some can use light as an energy source using the light-driven proton pump bacteriorhodopsin. As a consequence cell components like proteins nucleic acids and membranes.

Question Video Classifying Organisms As Archaea Or Bacteria Nagwa

Thermophilic Archaea Yellowstone National Park U S National Park Service

A Microbe S Membrane Helps It Survive Extreme Environments Stanford News
Comments
Post a Comment